728x90

Given an m x n matrix, return all elements of the matrix in spiral order.
Example 1:
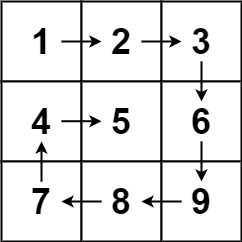
Input: matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
Output: [1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
Example 2:
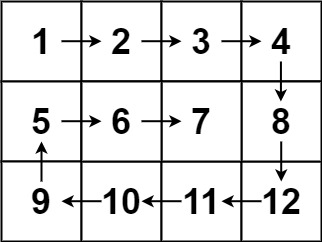
Input: matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]]
Output: [1,2,3,4,8,12,11,10,9,5,6,7]
Constraints:
- m == matrix.length
- n == matrix[i].length
- 1 <= m, n <= 10
- -100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100
Code :
var spiralOrder = function(matrix) {
// 행렬의 행과 열의 길이를 구합니다.
const m = matrix.length;
const n = matrix[0].length;
// 결과를 저장할 배열을 선언합니다.
const result = [];
// 행렬을 나선형으로 읽기 위한 시작과 끝 인덱스를 설정합니다.
let startRow = 0;
let endRow = m - 1;
let startCol = 0;
let endCol = n - 1;
// 시작과 끝 인덱스가 교차할 때까지 반복합니다.
while (startRow <= endRow && startCol <= endCol) {
// 윗 행을 읽습니다.
for (let i = startCol; i <= endCol; i++) {
result.push(matrix[startRow][i]);
}
startRow++;
// 오른쪽 열을 읽습니다.
for (let i = startRow; i <= endRow; i++) {
result.push(matrix[i][endCol]);
}
endCol--;
// 아랫 행을 읽습니다.
if (startRow <= endRow) {
for (let i = endCol; i >= startCol; i--) {
result.push(matrix[endRow][i]);
}
endRow--;
}
// 왼쪽 열을 읽습니다.
if (startCol <= endCol) {
for (let i = endRow; i >= startRow; i--) {
result.push(matrix[i][startCol]);
}
startCol++;
}
}
// 나선형으로 정렬된 행렬의 모든 요소를 반환합니다.
return result;
};
Solutions Code :
var spiralOrder = function(matrix) {
// MATRIX[Y][X]
// ---------
//Y0 | 1 2 3 |
//Y1 | 4 5 6 |
//Y2 | 7 8 9 |
// ---------
// X0 X1 X2
// 주어진 2D 행렬의 세로와 가로 길이를 각각 yLength와 xLength에 저장
const yLength = matrix.length, xLength = matrix[0].length;
// 현재 위치를 표현하는 변수
let y = 0, x = 0;
// 순회한 요소의 개수를 세는 변수
let count = 0;
// 전체 행렬의 요소 개수
const area = xLength * yLength;
// 결과를 저장할 배열
let bag = [];
// 모든 요소를 순회할 때까지 반복
while (count < area) {
// 왼쪽에서 오른쪽으로 이동
for (let i = x; count < area && i < xLength - x; i++) {
bag.push(matrix[y][i]);
count++;
}
y++;
// 위에서 아래로 이동
for (let i = y; count < area && i < yLength - y + 1; i++) {
bag.push(matrix[i][(xLength - 1) - x]);
count++;
}
x++;
// 오른쪽에서 왼쪽으로 이동
for (let i = (xLength - 1) - x; count < area && i >= x - 1; i--) {
bag.push(matrix[(yLength - 1) - (y - 1)][i]);
count++;
}
// 아래에서 위로 이동
for (let i = (yLength - 1) - y; count < area && i >= y; i--) {
bag.push(matrix[i][x - 1]);
count++;
}
}
// 결과 배열 반환
return bag;
};
출처 : https://leetcode.com/problemset/all/
Problems - LeetCode
Boost your coding interview skills and confidence by practicing real interview questions with LeetCode. Our platform offers a range of essential problems for practice, as well as the latest questions being asked by top-tier companies.
leetcode.com
728x90
'LeetCode' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [LeetCode] 56. Merge Intervals (0) | 2023.12.27 |
|---|---|
| [LeetCode] 55. Jump Game (2) | 2023.12.26 |
| Leethub 연동 에러 및 해결 방법 (2) | 2023.12.22 |
| [LeetCode] 53. Maximum Subarray (2) | 2023.12.22 |
| [LeetCode] 52. N-Queens II (2) | 2023.12.22 |



